As extra practice point slope and slope intercept form takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of linear equations, equipping readers with a thorough understanding of slope-intercept and point-slope forms. Through engaging explanations, practical examples, and ample practice problems, learners will gain a solid foundation in this essential mathematical concept.
Extra Practice: Point-Slope and Slope-Intercept Form: Extra Practice Point Slope And Slope Intercept Form
In this extra practice, we will explore the point-slope form and slope-intercept form of linear equations. We will solve practice problems involving converting between these forms and graphing linear equations.
Point-Slope Form
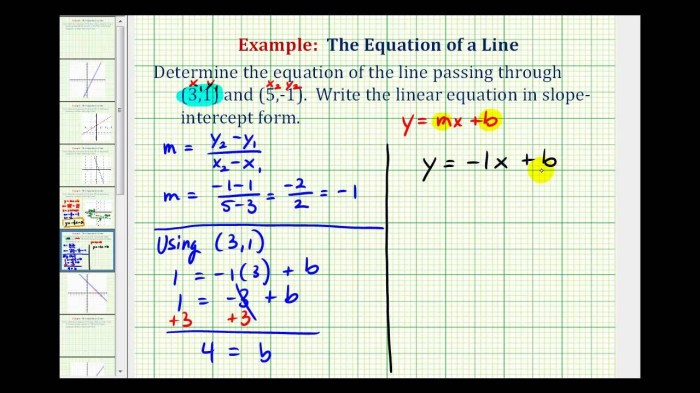
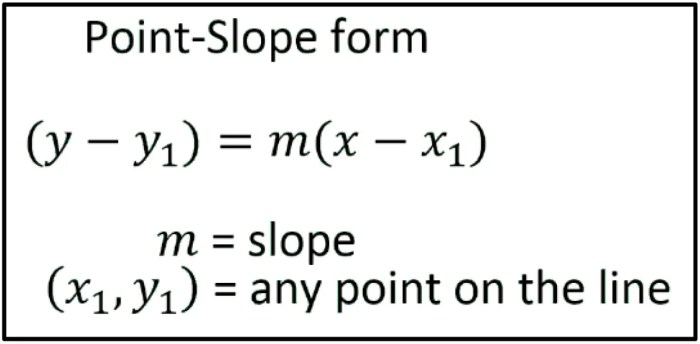
The point-slope form of a linear equation is:
y
- y1= m(x
- x 1)
where (x 1, y 1) is a point on the line and m is the slope of the line.
For example, the equation y – 2 = 3(x – 1) is in point-slope form. The point (1, 2) is on the line and the slope is 3.
To convert from point-slope form to slope-intercept form, we solve for y:
y = mx + y1
mx1
Slope-Intercept Form
The slope-intercept form of a linear equation is:
y = mx + b
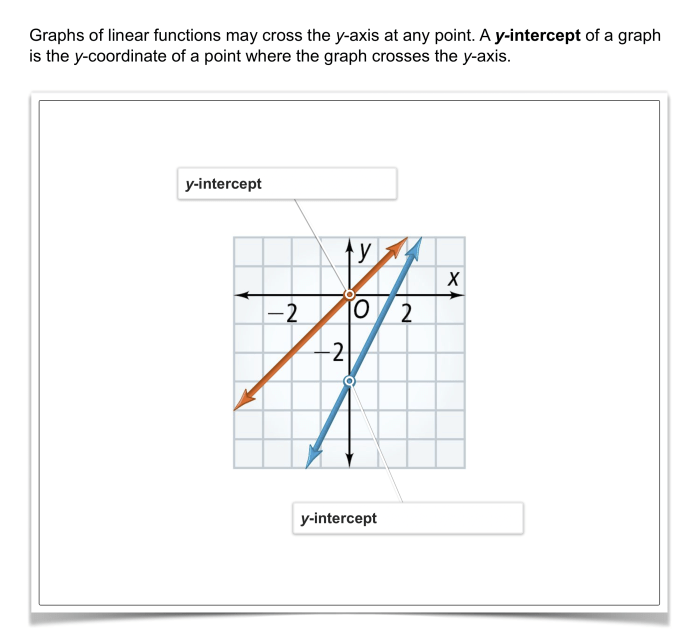
where m is the slope of the line and b is the y-intercept (the value of y when x = 0).
For example, the equation y = 2x + 3 is in slope-intercept form. The slope is 2 and the y-intercept is 3.
To convert from slope-intercept form to point-slope form, we solve for y – y 1:
y
- y1= m(x
- x 1)
Extra Practice Problems, Extra practice point slope and slope intercept form
| Equation in Slope-Intercept Form | Equation in Point-Slope Form | Graph of the Equation |
|---|---|---|
| y = 2x + 1 | y
|
[Gambar grafik garis y = 2x + 1] |
y =
|
y
|
[Gambar grafik garis y =
|
y = 3x
|
y + 2 = 3(x + 1) | [Gambar grafik garis y = 3x
|
Solve the following problems:
- Convert the equation y = 2x + 1 to point-slope form using the point (1, 3).
- Convert the equation y
- 3 =
- 1(x
- 2) to slope-intercept form.
- Graph the equation y = 3x
2.
FAQ Guide
What is the difference between slope-intercept form and point-slope form?
Slope-intercept form (y = mx + b) expresses a linear equation in terms of its slope (m) and y-intercept (b), while point-slope form (y – y1 = m(x – x1)) uses a specific point (x1, y1) and the slope to define the line.
How do I convert between slope-intercept form and point-slope form?
To convert from slope-intercept form to point-slope form, substitute the values of m and b into the point-slope formula. To convert from point-slope form to slope-intercept form, solve for y and simplify to the form y = mx + b.
Why is understanding slope-intercept form important?
Slope-intercept form is crucial because it allows us to easily determine the slope and y-intercept of a line, which are essential for graphing, analyzing, and solving linear equations.