Embarking on the exploration of the spread of pathogens worksheet, we delve into the intricacies of disease transmission and the measures employed to mitigate its impact. This comprehensive resource unravels the complex mechanisms governing pathogen behavior, shedding light on the factors that influence their spread and the strategies we can implement to safeguard public health.
Within this worksheet, we embark on a journey of discovery, examining the diverse types of pathogens and their unique characteristics. We investigate the environmental and behavioral factors that contribute to their proliferation, unraveling the modes of transmission that enable them to spread from one host to another.
Moreover, we delve into the principles of pathogen prevention and control, exploring the measures we can take to minimize their impact on human health.
Definition and Types of Pathogens

Pathogens are microorganisms or agents that cause disease in their host. They can be classified based on their size, structure, and mode of replication.
Types of Pathogens
- Bacteria: Single-celled prokaryotic organisms that can cause a wide range of infections.
- Viruses: Non-cellular entities that require a host cell to replicate.
- Fungi: Eukaryotic organisms that can cause skin, nail, and systemic infections.
- Parasites: Organisms that live on or in a host organism and derive nutrients from it.
Factors Influencing the Spread of Pathogens
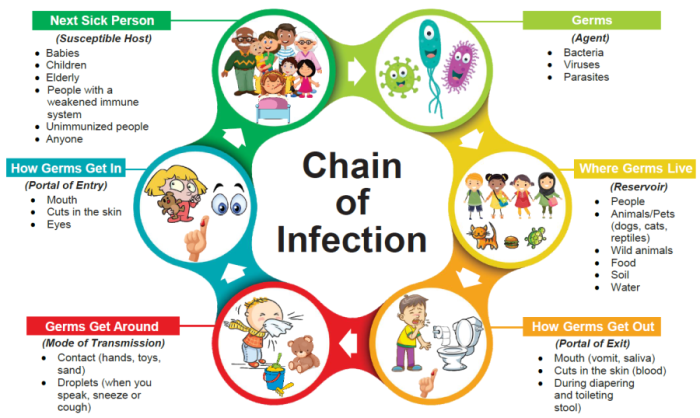
The spread of pathogens is influenced by various factors, including environmental conditions and human behavior.
Environmental Factors
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect pathogen survival and transmission.
- Humidity: High humidity can promote the growth and transmission of certain pathogens.
- Sunlight: Ultraviolet radiation can kill or inactivate pathogens.
Human Behavior
- Hygiene practices: Poor hygiene can facilitate the spread of pathogens.
- Travel: Travel can increase the risk of exposure to new pathogens.
- Contact with infected individuals: Close contact with infected individuals can transmit pathogens.
Healthcare Systems and Public Health Measures
- Surveillance: Monitoring the spread of pathogens is essential for early detection and response.
- Vaccination: Vaccination can protect individuals from specific pathogens.
- Isolation: Isolating infected individuals can prevent further transmission.
Modes of Transmission
Pathogens can be transmitted through various modes, including airborne, contact, and vector-borne transmission.
Airborne Transmission
- Pathogens are expelled into the air through coughing or sneezing.
- Example: Influenza virus
Contact Transmission
- Pathogens are transmitted through direct or indirect contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces.
- Example: Staphylococcus aureus
Vector-borne Transmission, The spread of pathogens worksheet
- Pathogens are transmitted by vectors such as mosquitoes, ticks, or fleas.
- Example: Malaria parasite
Prevention and Control Strategies
Preventing and controlling the spread of pathogens requires a multifaceted approach.
General Principles
- Hand hygiene: Washing hands with soap and water is crucial for preventing pathogen transmission.
- Vaccination: Vaccination protects individuals from specific pathogens.
- Isolation: Isolating infected individuals prevents further transmission.
Specific Measures
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections.
- Antiviral medications: Antiviral medications are used to treat viral infections.
- Surveillance: Monitoring the spread of pathogens allows for early detection and response.
Consequences of Pathogen Spread
The spread of pathogens can have significant consequences for individuals and society.
Health Consequences
- Morbidity: Pathogens can cause a wide range of illnesses, from mild to life-threatening.
- Mortality: Pathogens can lead to death in severe cases.
- Long-term effects: Some pathogens can cause long-term health problems, such as chronic fatigue syndrome.
Economic and Social Impacts
- Healthcare costs: Pathogen-related illnesses can strain healthcare systems and increase costs.
- Productivity loss: Illnesses can lead to absenteeism from work or school.
- Social stigma: Pathogen-related illnesses can lead to social stigma and discrimination.
Historical and Recent Pandemics
- 1918 influenza pandemic: Killed an estimated 50-100 million people worldwide.
- COVID-19 pandemic: An ongoing global pandemic that has caused significant morbidity and mortality.
Role of Education and Awareness: The Spread Of Pathogens Worksheet
Educating the public about pathogen spread and prevention is crucial for reducing transmission.
Importance of Education
- Empowering individuals: Education empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
- Changing behavior: Education can change behavior and promote healthy practices.
- Reducing stigma: Education can reduce stigma associated with pathogen-related illnesses.
Disseminating Information
- Public health campaigns: Public health campaigns can raise awareness and disseminate information about pathogen prevention.
- School programs: School programs can teach children about pathogen transmission and prevention.
- Community outreach: Community outreach programs can reach underserved populations with health information.
Successful Initiatives
- Handwashing campaigns: Handwashing campaigns have been successful in reducing the spread of diarrheal diseases.
- Vaccination programs: Vaccination programs have significantly reduced the incidence of preventable diseases.
- HIV/AIDS awareness campaigns: HIV/AIDS awareness campaigns have raised awareness and reduced stigma associated with the disease.
Essential FAQs
What are the most common types of pathogens?
Bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites are the most prevalent types of pathogens.
How can I protect myself from pathogens?
Practicing good hygiene, such as handwashing and covering your mouth when you cough or sneeze, can significantly reduce your risk of exposure to pathogens.
What are the most effective ways to control the spread of pathogens?
Vaccination, surveillance, and outbreak management are crucial strategies for controlling the spread of pathogens.