Energy through an ecosystem worksheet delves into the intricate mechanisms by which energy flows through various levels of ecological communities, shaping their dynamics and influencing their stability. This comprehensive guide unravels the fundamental concepts of energy transfer, revealing the interconnectedness of organisms and their environments.
Within ecosystems, energy cascades from producers to consumers and decomposers, fueling the intricate web of life. Energy pyramids illustrate the gradual reduction of energy available at each trophic level, highlighting the importance of energy efficiency in ecosystem functioning. Understanding these principles empowers us to mitigate human impacts on energy flow, ensuring the health and resilience of our planet’s ecosystems.
Energy Flow through Ecosystems: Energy Through An Ecosystem Worksheet
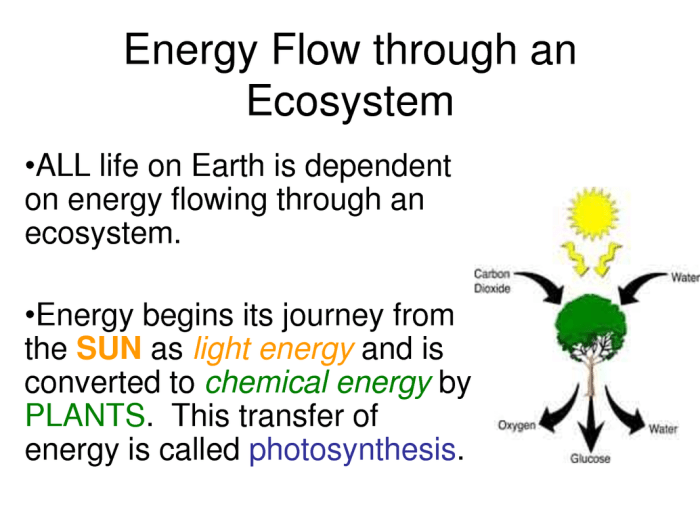
Energy flow through ecosystems refers to the transfer of energy from one organism to another within an ecosystem.
Energy enters ecosystems through producers, which are organisms that can convert inorganic matter into organic matter through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Consumers are organisms that cannot produce their own food and must consume other organisms to obtain energy. Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organisms and return nutrients to the ecosystem.
Energy Transfer between Trophic Levels
Energy is transferred between trophic levels within an ecosystem. A trophic level is a group of organisms that occupy the same level in a food chain and have similar feeding habits.
| Trophic Level | Organisms | Energy Source | Energy Transfer Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Producers | Plants, algae | Sunlight | 100% |
| Primary Consumers | Herbivores | Plants | 10% |
| Secondary Consumers | Carnivores | Herbivores | 1% |
| Tertiary Consumers | Top predators | Carnivores | 0.1% |
Energy Pyramids
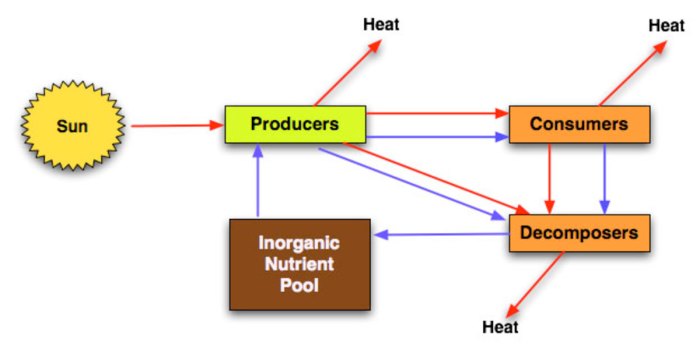
Energy pyramids are graphical representations of the amount of energy at each trophic level in an ecosystem. They are important for understanding ecosystem dynamics because they show how energy flows through the ecosystem and how much energy is available to organisms at each level.
Energy pyramids are typically drawn as a series of horizontal bars, with the bottom bar representing the producers (plants) and each subsequent bar representing a higher trophic level (herbivores, carnivores, etc.). The height of each bar represents the amount of energy available at that trophic level.
Limitations and Exceptions
Energy pyramids are a useful tool for understanding ecosystem dynamics, but they have some limitations. One limitation is that they do not take into account the efficiency of energy transfer between trophic levels. In other words, they do not show how much energy is lost as heat at each trophic level.
Another limitation is that energy pyramids do not always take into account the role of decomposers. Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organisms and return nutrients to the ecosystem. They play an important role in the cycling of energy and nutrients, but they are not always included in energy pyramids.
Despite these limitations, energy pyramids are a valuable tool for understanding ecosystem dynamics. They provide a visual representation of the flow of energy through an ecosystem and can help to identify potential problems in the ecosystem.
Energy Efficiency in Ecosystems
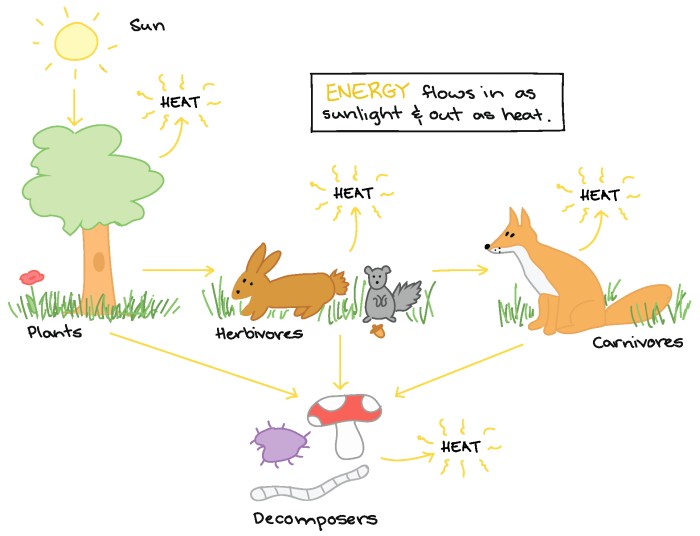
Energy efficiency in ecosystems refers to the ability of organisms to capture, store, and utilize energy from their environment in a manner that minimizes energy loss. It is a critical aspect of ecosystem functioning, as it influences the productivity, stability, and resilience of ecosystems.
Organisms have evolved various adaptations to maximize energy efficiency. These include:
Adaptations for Energy Efficiency
- Physiological adaptations:These include efficient metabolic pathways, insulation to reduce heat loss, and adaptations for nutrient absorption.
- Behavioral adaptations:These include foraging strategies, migration patterns, and social interactions that minimize energy expenditure.
- Morphological adaptations:These include body size, shape, and surface area that influence energy capture and utilization.
Factors influencing energy efficiency within ecosystems include:
Factors Influencing Energy Efficiency
- Environmental conditions:Temperature, light availability, and resource availability can affect the energy efficiency of organisms.
- Competition:Competition for resources can drive organisms to evolve adaptations that enhance energy efficiency.
- Predation:The presence of predators can influence the energy efficiency of prey species, as they may need to allocate more energy to predator avoidance.
Energy and Nutrient Cycling
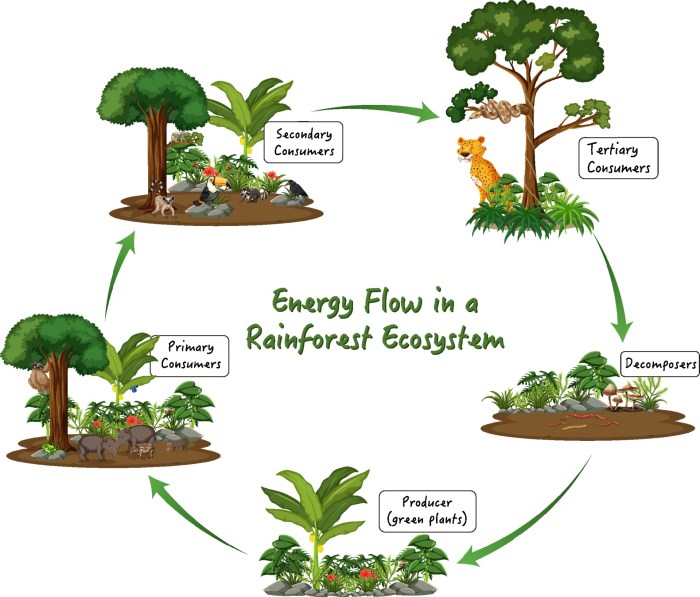
Energy flow and nutrient cycling are intricately connected processes in ecosystems. Energy from the sun fuels the cycling of nutrients, which in turn supports the flow of energy through the ecosystem.
Nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon, are essential for plant growth and the production of organic matter. Decomposers, primarily bacteria and fungi, play a crucial role in nutrient recycling by breaking down dead plants and animals, releasing nutrients back into the soil or water for reuse by plants.
Role of Decomposers
- Decomposers break down organic matter into simpler compounds, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem.
- They contribute to the formation of humus, a nutrient-rich organic material that improves soil fertility.
- Decomposers also release carbon dioxide during the decomposition process, contributing to the carbon cycle.
Human Impact on Energy Flow
Human activities significantly disrupt energy flow in ecosystems, leading to imbalances and potential ecosystem collapse. Understanding these impacts is crucial for devising mitigation strategies to preserve ecological integrity.
Deforestation, Energy through an ecosystem worksheet
Deforestation removes vast areas of vegetation, which are primary producers that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. This loss reduces the amount of energy available to other organisms, disrupting food chains and energy pyramids.
Agriculture
Modern agricultural practices rely heavily on fertilizers and pesticides, which can alter nutrient cycling and energy flow. Excessive fertilizer use can lead to eutrophication, where excessive nutrients cause algal blooms and disrupt oxygen levels.
Pollution
Pollution, such as air pollution from fossil fuel combustion and water pollution from industrial waste, can harm organisms and disrupt energy flow. Pollutants can alter plant growth, reduce photosynthetic efficiency, and accumulate in the food chain, affecting higher trophic levels.
Climate Change
Climate change, driven by human activities, is altering temperature and precipitation patterns, leading to shifts in species distribution and energy availability. Warmer temperatures can increase metabolic rates and alter food availability, while changes in precipitation can affect plant growth and water availability for organisms.
Mitigation Strategies
Mitigating human impacts on energy flow requires a multifaceted approach:
- Promoting sustainable land-use practices, including reforestation and reducing deforestation.
- Implementing sustainable agricultural practices, such as organic farming and precision agriculture.
- Reducing pollution through emission controls and waste management.
- Addressing climate change through mitigation and adaptation measures.
- Educating the public about the importance of energy flow and the impacts of human activities.
Key Questions Answered
What is the significance of energy flow in ecosystems?
Energy flow provides the energy necessary for organisms to survive, grow, and reproduce, driving the entire ecological community.
How do energy pyramids represent energy flow?
Energy pyramids depict the decreasing amount of energy available at each trophic level, highlighting the energy loss during transfer.
What is the role of decomposers in energy flow?
Decomposers break down dead organisms, releasing nutrients and energy back into the ecosystem, completing the energy cycle.